Knee Pain and Hip Weakness: What Came First?

If you’re experiencing knee pain and hip weakness, you may be wondering which condition came first. The truth is that knee pain and hip weakness are often interrelated, and one can contribute to the other.
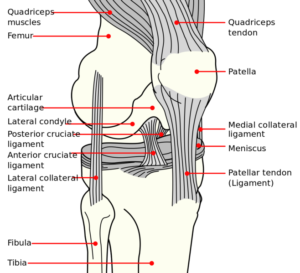
Diagram of knee. Image courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
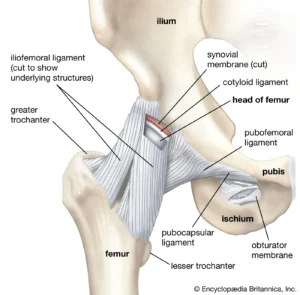
Diagram of a hip. Image courtesy of Britannica.
When you walk or run, your hip muscles, including your glutes, play an important role in stabilizing your pelvis and controlling the movement of your legs. Weakness in these muscles can cause compensations and changes in movement patterns that can put extra stress on the knees. This can lead to pain and inflammation in the knee joint.
Conversely, knee pain can also contribute to hip weakness. When you have pain in your knee, you may compensate by shifting your weight to the other leg or altering your gait pattern. This can cause weakness and imbalance in the hip muscles over time.
At Barrhaven Health HUB, we take a comprehensive approach to knee pain and hip weakness. Our team of experienced therapists will assess your symptoms and movement patterns to determine the underlying cause of your pain and weakness. We’ll work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses both the knee pain and hip weakness.
Treatment may include exercises to strengthen the hip muscles, as well as manual therapy techniques to reduce pain and improve range of motion. We may also recommend the use of orthotics or other supportive devices to help correct any imbalances in your gait.
Don’t let knee pain and hip weakness hold you back from doing the activities you love. Contact us at Barrhaven Health HUB to learn more about our approach to knee pain and hip weakness and to schedule an appointment with one of our experienced therapists.
Book your appointment here: https://barrhavenhealthhub.janeapp.com/
Additional links for more information:
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/knee-pain/symptoms-causes/syc-20350849
