Plantar Fasciitis and the Fallen Arch: To Support or Not to Support, That is the Question?

If you’re experiencing pain in the bottom of your foot, especially around the heel, it could be a sign of plantar fasciitis. Plantar fasciitis is a common condition that affects the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that connects the heel bone to the toes. One common contributing factor to plantar fasciitis is a fallen arch, also known as flat feet.
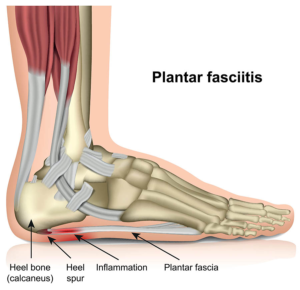
Plantar Fasciitis. Image courtesy of Healthdirect
So, when it comes to managing plantar fasciitis with a fallen arch, the question arises: should you use arch supports or not? The answer depends on the individual and their specific needs.
At Barrhaven Health HUB, our experienced therapists can assess your condition and determine whether arch supports or other treatments are necessary to manage your plantar fasciitis. In some cases, arch supports can help to reduce pain and support the arch of the foot, especially during activities that put stress on the feet.
However, in other cases, arch supports may not be necessary or may even exacerbate the problem. For example, if the arch supports are not properly fitted or are too rigid, they can put additional stress on the plantar fascia and exacerbate the condition.
In addition to arch supports, it is common that we recommend specific stretching and strengthening exercises, manual therapy, acupuncture, and modalities like extracorporeal shockwave to help reduce pain and promote healing.
Think you may have plantar fasciitis? Take a minute to get some expert help with one of our Physiotherapists, we can provide a thorough assessment and show you the best course of action for managing your plantar fasciitis.
Book your appointment here: https://barrhavenhealthhub.janeapp.com/
Here are some additional links for more information:
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/plantar-fasciitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20354846
